Draw Diagonal Heatmap with R
In bioinformatics research, sometimes we need to draw a diagonal heatmap if we want to display the variations within a grid. We need to “split” each grid by diagonal such that the upper triangle and the lower triangle can each represent a value. Since there are no existing package that performs the task, we can use ggplot2 to draw it from scratch.
Draw a triangle
First we can use geom_polygon to draw one single triangle.
## lower triangle data
cone1 = data.frame(x = c(1,2,2),
y = c(1,1,2))
## plot lower triangle
cone1 %>%
ggplot(aes(x=x, y=y)) +
geom_polygon(fill="#213c18")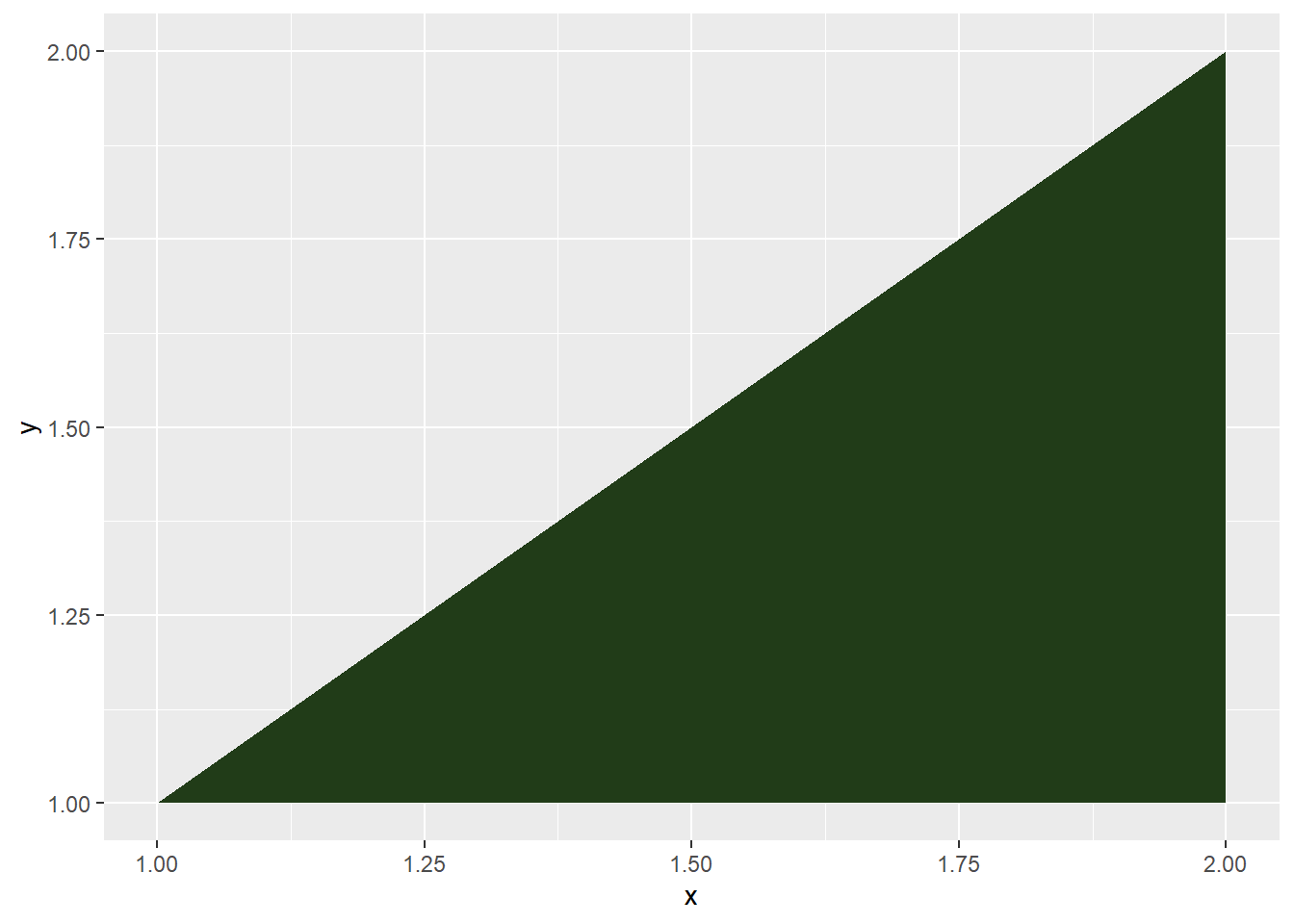
## upper triangble data
cone2 = data.frame(x = c(1,1,2),
y = c(1,2,2))
## plot upper triangle
cone2 %>%
ggplot(aes(x=x, y=y)) +
geom_polygon(fill = "#668c6f")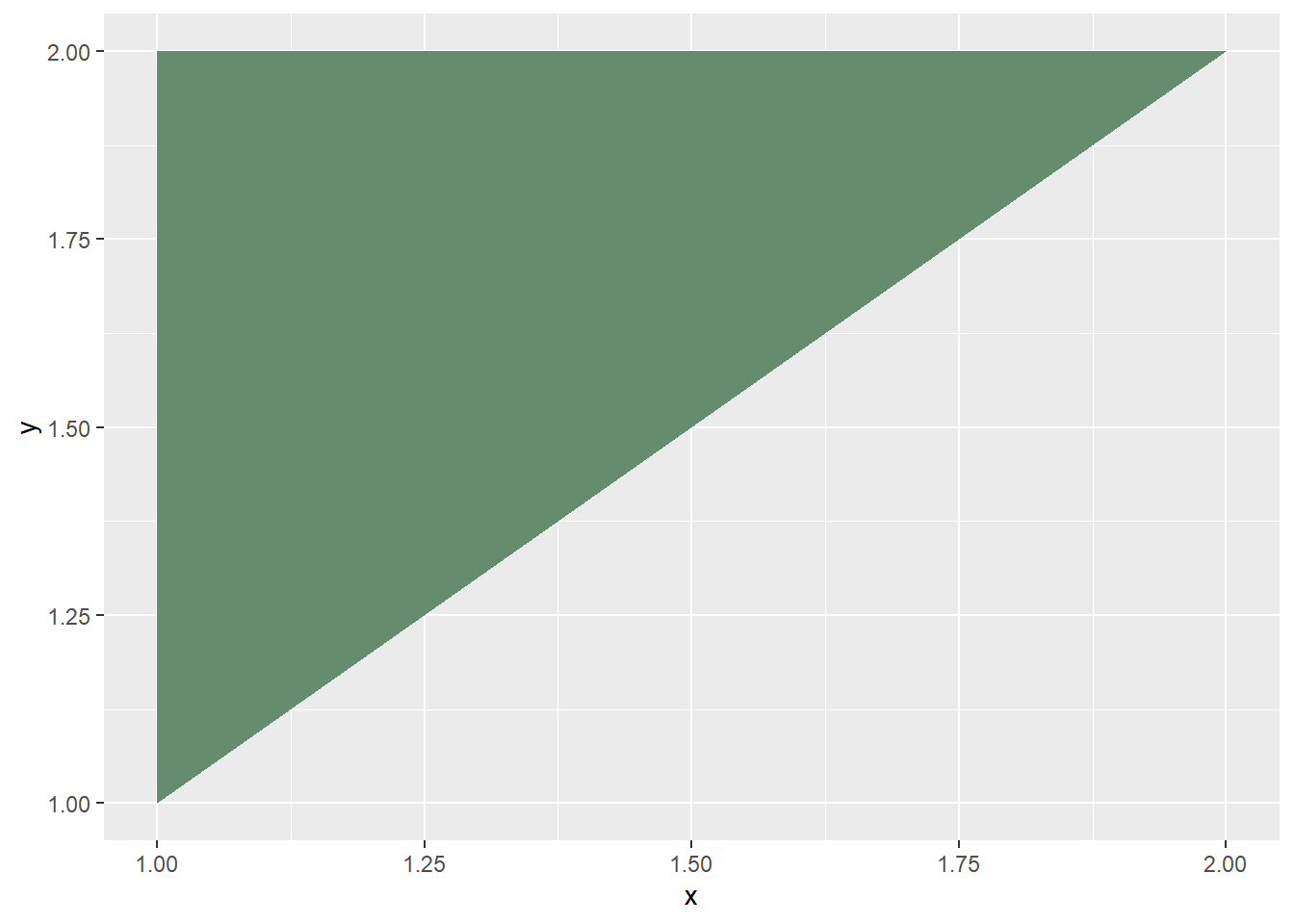
# combine to form basic block
cone1 %>%
ggplot(aes(x=x, y=y)) +
geom_polygon(fill="#213c18")+
geom_polygon(data=cone2, fill = "#668c6f")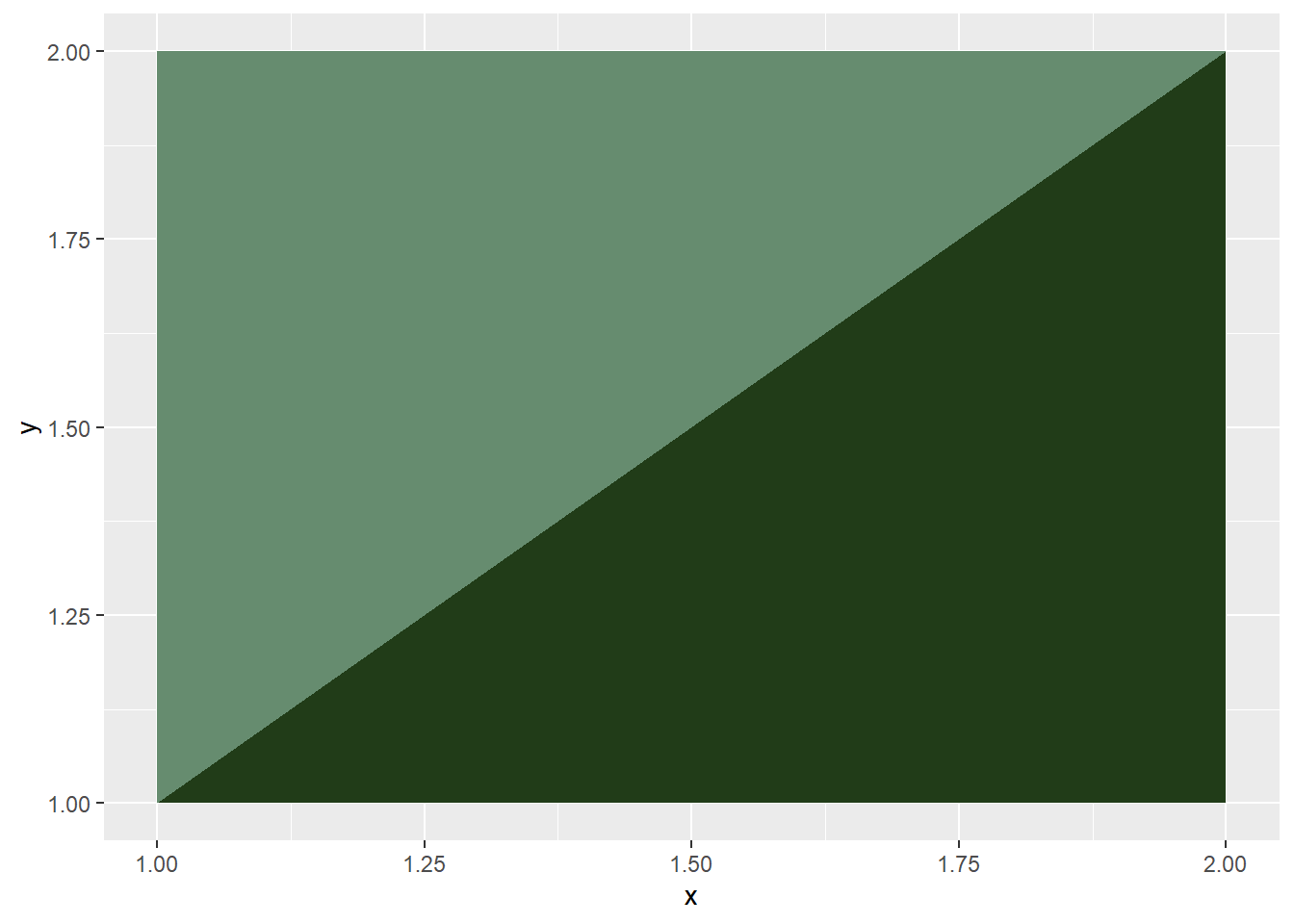
Use Function to Generate Triangles
Then we will use a function to plot all the triangles.
trianle <- function(a,b,type="up"){
## single lower triangle
trianle_down <- function(a,b){
data.frame(x=c(0,1,1)+a,
y= c(0,0,1)+b,
group=paste0(a,"_",b),
stringsAsFactors = F)
}
## single upper triangle
trianle_up <- function(a,b){
data.frame(x=c(0,0,1)+a,
y= c(0,1,1)+b,
group=paste0(a,"_",b),
stringsAsFactors = F)
}
### all upper triangles
if(type=="up"){
data <- do.call(rbind,lapply(1:b, function(i){
do.call(rbind,lapply(1:a,trianle_up,i))
}))
}
### all lower triangles
if(type=="down"){
data <- do.call(rbind,lapply(1:b, function(i){
do.call(rbind,lapply(1:a,trianle_down,i))
}))
}
return(data)
}# create triangle data
updata <- trianle(33,20,"up")
downdata <- trianle(33,20,"down")# plot all upper triangles
updata %>%
ggplot(aes(x=x, y=y)) +
geom_polygon(aes(group=group,fill=group))+
theme(legend.position = "none")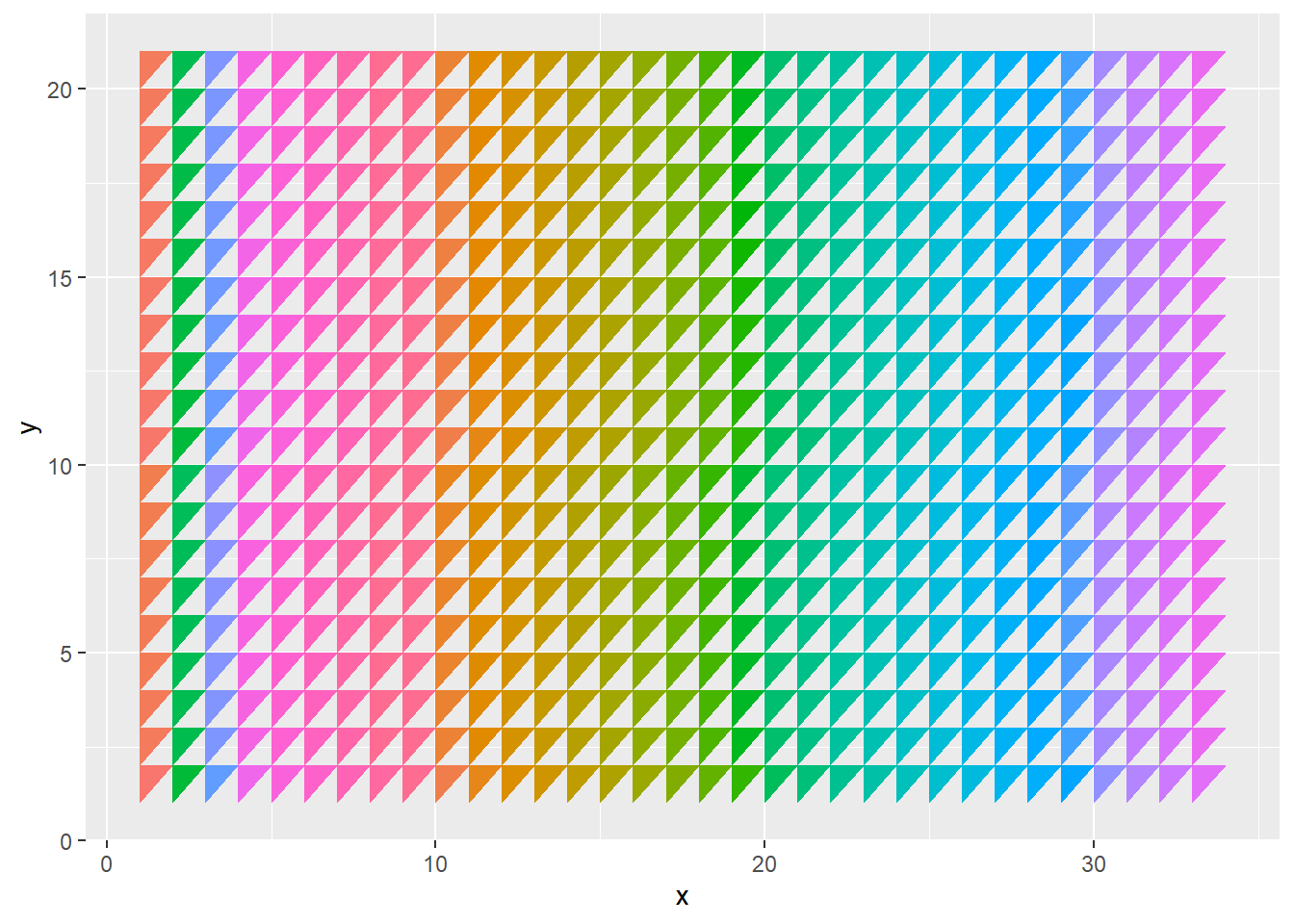
# plot all lower triangles
downdata %>%
ggplot(aes(x=x, y=y)) +
geom_polygon(aes(group=group,fill=group))+
theme(legend.position = "none")
Combining the two parts together, we can generate a plot of diagonal heatmap.